Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: How to Implement a Python Stack
Have you heard of stacks and wondered what they are? Do you have the general idea but are wondering how to implement a Python stack? You’ve come to the right place!
In this tutorial, you’ll learn:
- How to recognize when a stack is a good choice for data structures
- How to decide which implementation is best for your program
- What extra considerations to make about stacks in a threading or multiprocessing environment
This tutorial is for Pythonistas who are comfortable running scripts, know what a list is and how to use it, and are wondering how to implement Python stacks.
Free Bonus: Click here to get a Python Cheat Sheet and learn the basics of Python 3, like working with data types, dictionaries, lists, and Python functions.
What Is a Stack?
A stack is a data structure that stores items in an Last-In/First-Out manner. This is frequently referred to as LIFO. This is in contrast to a queue, which stores items in a First-In/First-Out (FIFO) manner.
It’s probably easiest to understand a stack if you think of a use case you’re likely familiar with: the Undo feature in your editor.
Let’s imagine you’re editing a Python file so we can look at some of the operations you perform. First, you add a new function. This adds a new item to the undo stack:
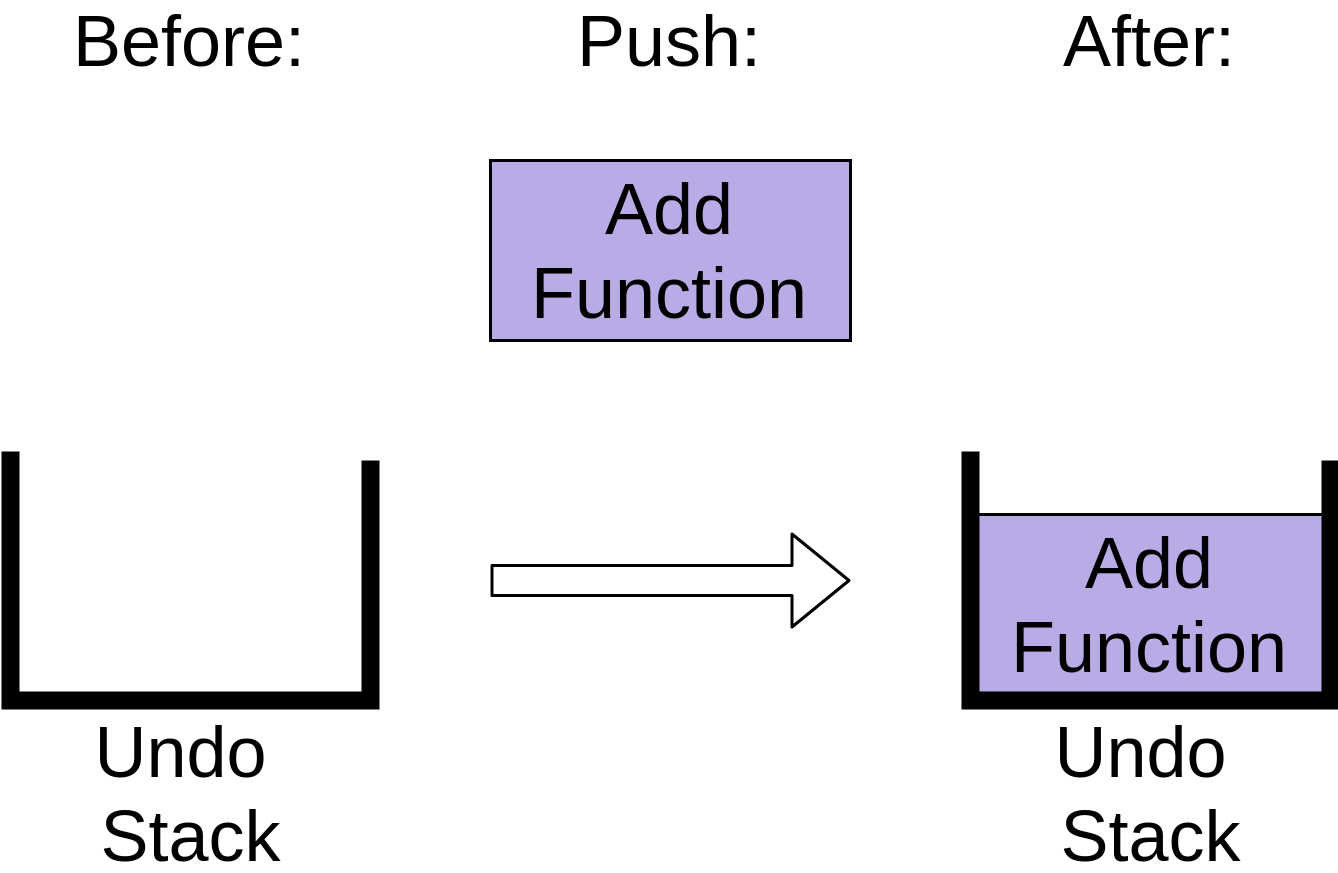
You can see that the stack now has an Add Function operation on it. After adding the function, you delete a word from a comment. This also gets added to the undo stack:
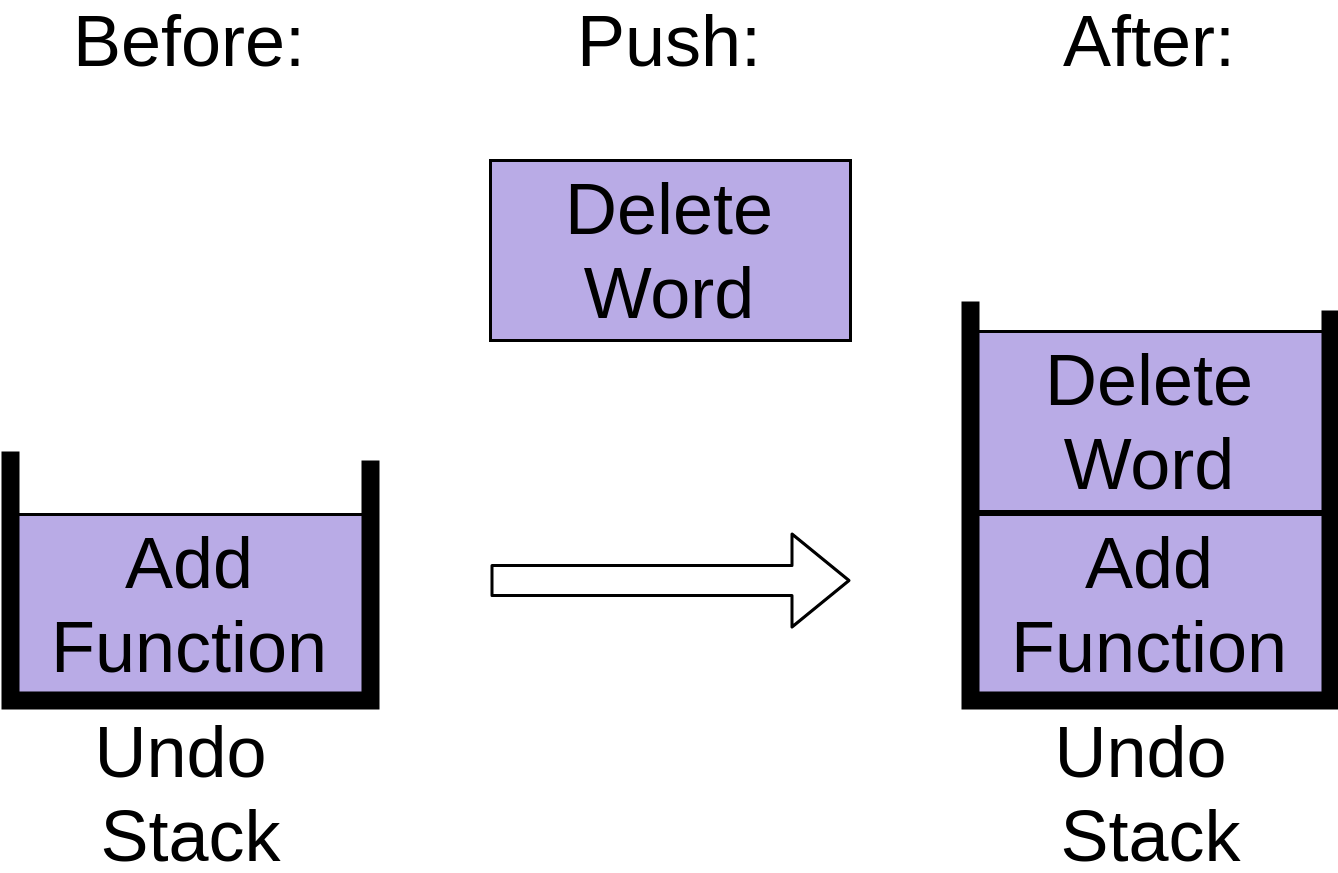
Notice how the Delete Word item is placed on top of the stack. Finally you indent a comment so that it’s lined up properly:
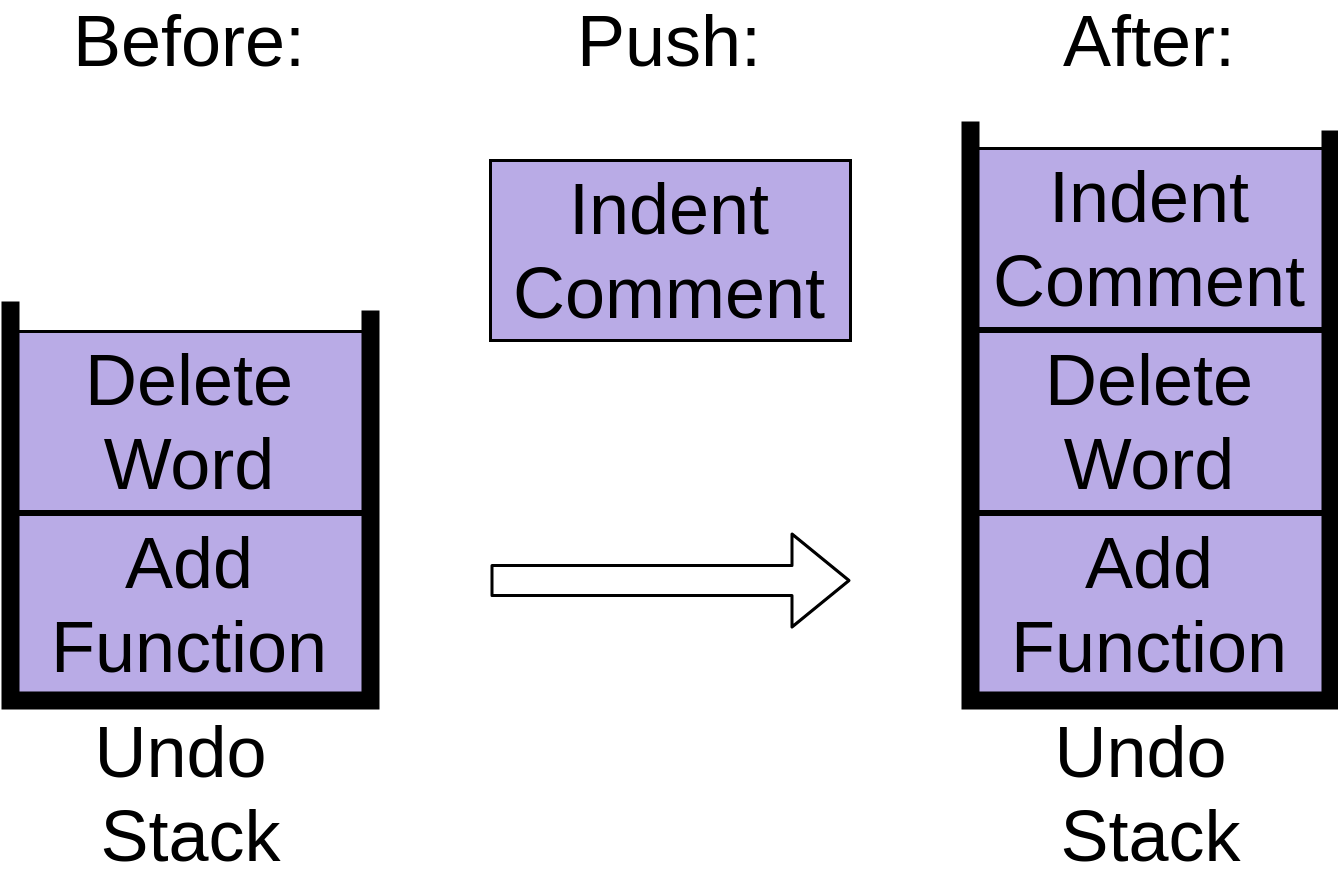
You can see that each of these commands are stored in an undo stack, with each new command being put at the top. When you’re working with stacks, adding new items like this is called push.
Now you’ve decided to undo all three of those changes, so you hit the undo command. It takes the item at the top of the stack, which was indenting the comment, and removes that from the stack:
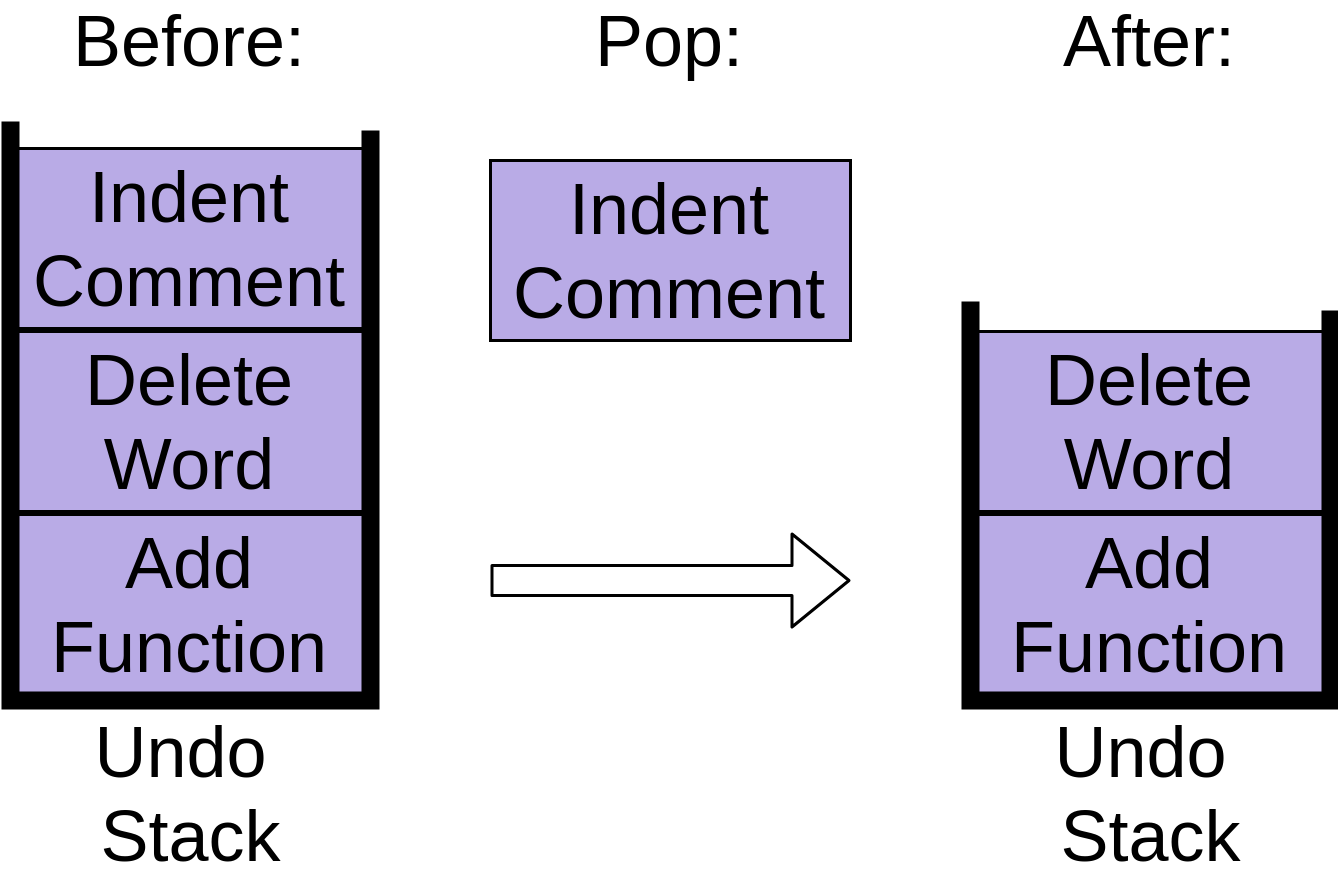
Your editor undoes the indent, and the undo stack now contains two items. This operation is the opposite of push and is commonly called pop.
When you hit undo again, the next item is popped off the stack:
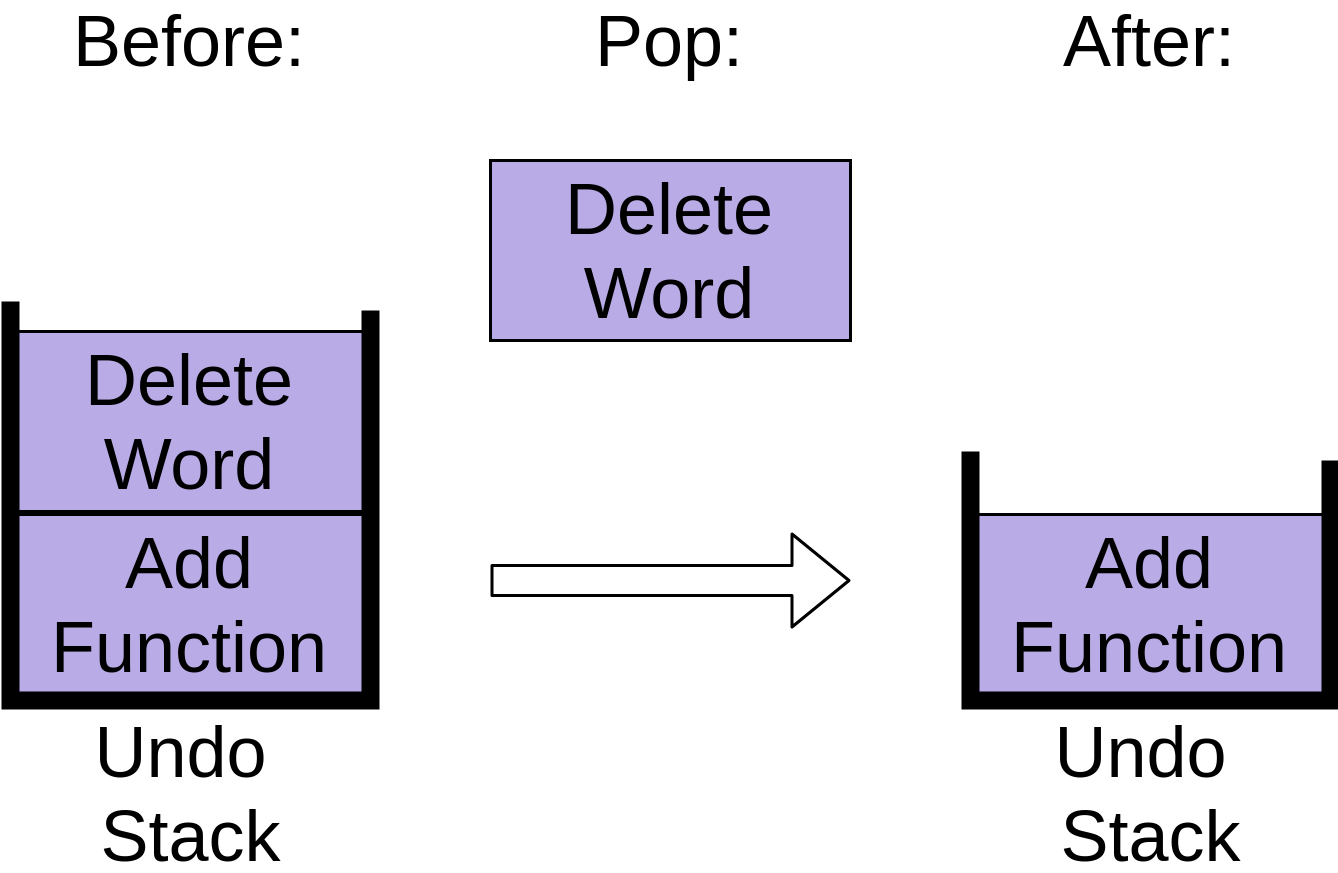
This removes the Delete Word item, leaving only one operation on the stack.
Finally, if you hit Undo a third time, then the last item will be popped off the stack:
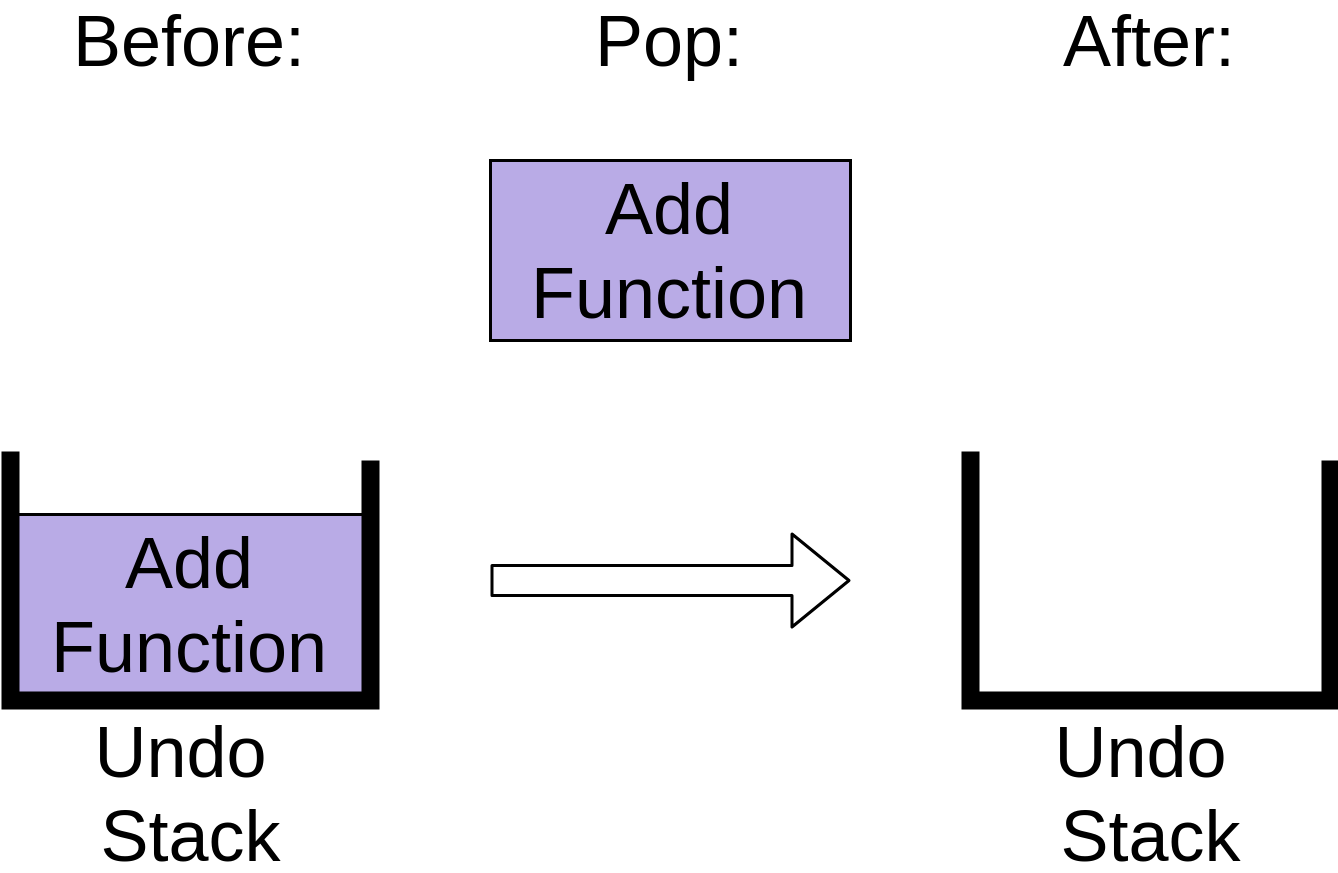
The undo stack is now empty. Hitting Undo again after this will have no effect because your undo stack is empty, at least in most editors. You’ll see what happens when you call .pop() on an empty stack in the implementation descriptions below.
Implementing a Python Stack
There are a couple of options when you’re implementing a Python stack. This article won’t cover all of them, just the basic ones that will meet almost all of your needs. You’ll focus on using data structures that are part of the Python library, rather than writing your own or using third-party packages.
You’ll look at the following Python stack implementations:
listcollections.dequequeue.LifoQueue
Using list to Create a Python Stack
The built-in list structure that you likely use frequently in your programs can be used as a stack. Instead of .push(), you can use .append() to add new elements to the top of your stack, while .pop() removes the elements in the LIFO order:
>>> myStack = []
>>> myStack.append('a')
>>> myStack.append('b')
>>> myStack.append('c')
>>> myStack
['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> myStack.pop()
'c'
>>> myStack.pop()
'b'
>>> myStack.pop()
'a'
>>> myStack.pop()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<console>", line 1, in <module>
IndexError: pop from empty list
You can see in the final command that a list will raise an IndexError if you call .pop() on an empty stack.
list has the advantage of being familiar. You know how it works and likely have used it in your programs already.
Unfortunately, list has a few shortcomings compared to other data structures you’ll look at. The biggest issue is that it can run into speed issues as it grows. The items in a list are stored with the goal of providing fast access to random elements in the list. At a high level, this means that the items are stored next to each other in memory.
If your stack grows bigger than the block of memory that currently holds it, then Python needs to do some memory allocations. This can lead to some .append() calls taking much longer than other ones.
There is a less serious problem as well. If you use .insert() to add an element to your stack at a position other than the end, it can take much longer. This is not normally something you would do to a stack, however.
The next data structure will help you get around the reallocation problem you saw with list.
Using collections.deque to Create a Python Stack
The collections module contains deque, which is useful for creating Python stacks. deque is pronounced “deck” and stands for “double-ended queue.”
You can use the same methods on deque as you saw above for list, .append(), and .pop():
>>> from collections import deque
>>> myStack = deque()
>>> myStack.append('a')
>>> myStack.append('b')
>>> myStack.append('c')
>>> myStack
deque(['a', 'b', 'c'])
>>> myStack.pop()
'c'
>>> myStack.pop()
'b'
>>> myStack.pop()
'a'
>>> myStack.pop()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<console>", line 1, in <module>
IndexError: pop from an empty deque
This looks almost identical to the list example above. At this point, you might be wondering why the Python core developers would create two data structures that look the same.
Why Have deque and list?
As you saw in the discussion about list above, it was built upon blocks of contiguous memory, meaning that the items in the list are stored right next to each other:
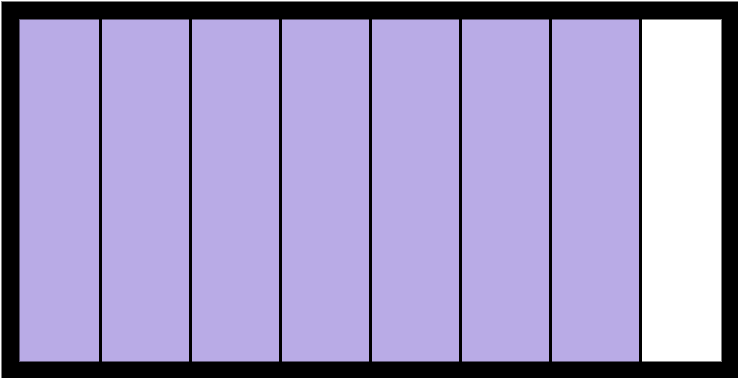
This works great for several operations, like indexing into the list. Getting myList[3] is fast, as Python knows exactly where to look in memory to find it. This memory layout also allows slices to work well on lists.
The contiguous memory layout is the reason that list might need to take more time to .append() some objects than others. If the block of contiguous memory is full, then it will need to get another block, which can take much longer than a normal .append():
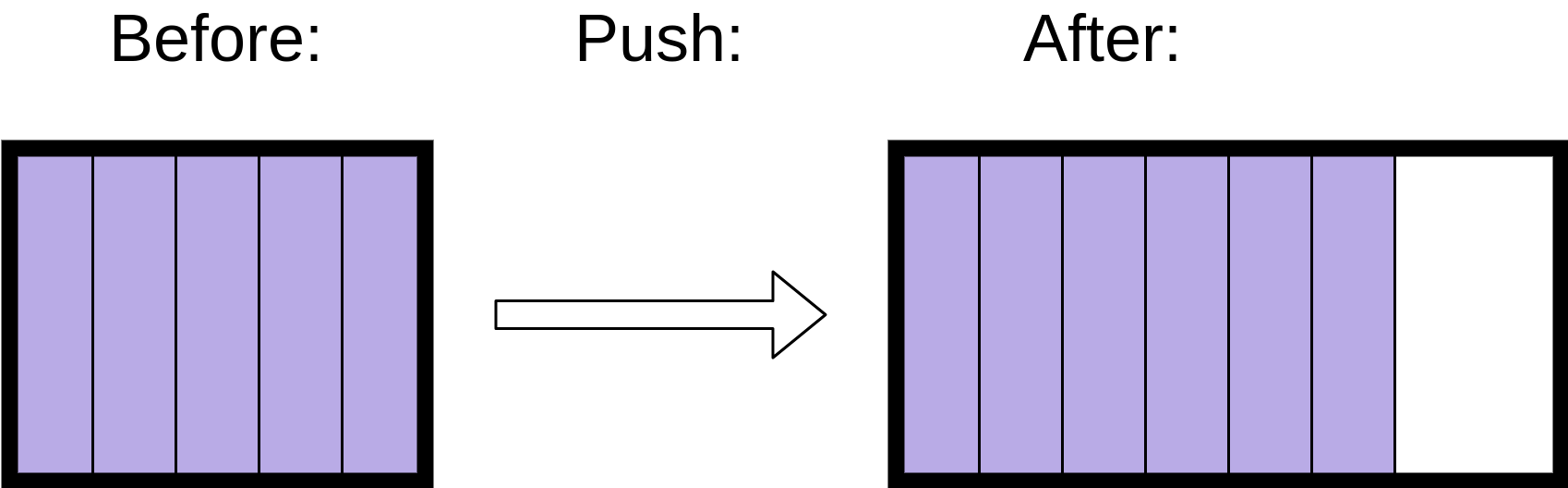
deque, on the other hand, is built upon a doubly linked list. In a linked list structure, each entry is stored in its own memory block and has a reference to the next entry in the list.
A doubly linked list is just the same, except that each entry has references to both the previous and the next entry in the list. This allows you to easily add nodes to either end of the list.
Adding a new entry into a linked list structure only requires setting the new entry’s reference to point to the current top of the stack and then pointing the top of the stack to the new entry:
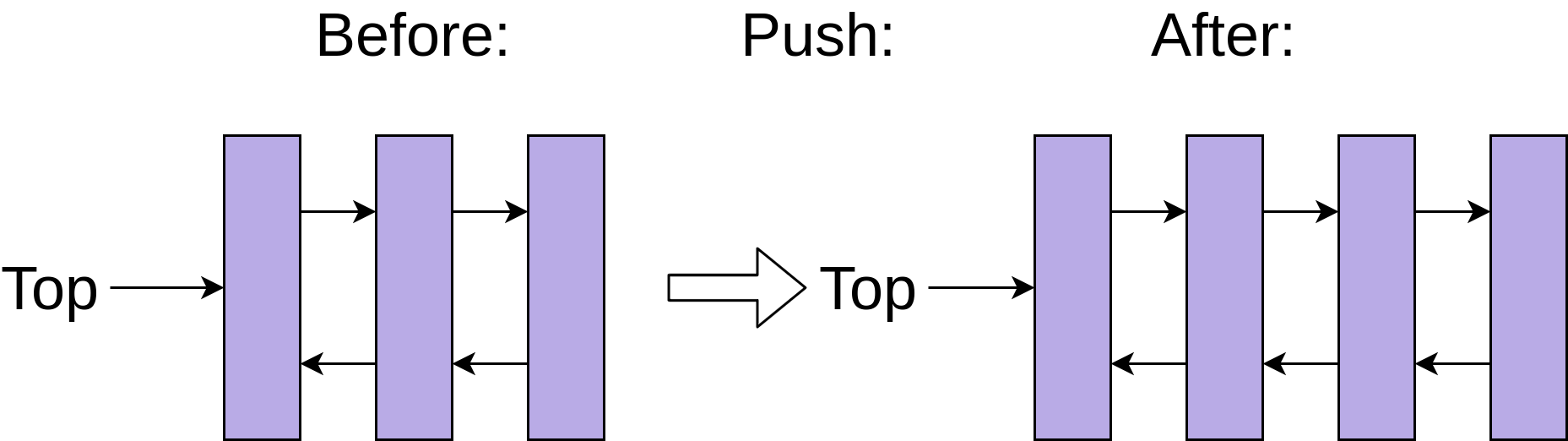
This constant-time addition and removal of entries onto a stack comes with a trade-off, however. Getting myDeque[3] is slower than it was for a list, because Python needs to walk through each node of the list to get to the third element.
Fortunately, you rarely want to do random indexing or slicing on a stack. Most operations on a stack are either push or pop.
The constant time .append() and .pop() operations make deque an excellent choice for implementing a Python stack if your code doesn’t use threading.
Python Stacks and Threading
Python stacks can be useful in multi-threaded programs as well, but if you’re not interested in threading, then you can safely skip this section and jump to the summary.
The two options you’ve seen so far, list and deque, behave differently if your program has threads.
To start with the simpler one, you should never use list for any data structure that can be accessed by multiple threads. list is not thread-safe.
Note: If you need a refresher on thread safety and race conditions, check out An Intro to Threading in Python.
deque is a little more complex, however. If you read the documentation for deque, it clearly states that both the .append() and .pop() operations are atomic, meaning that they won’t be interrupted by a different thread.
So if you restrict yourself to using only .append() and .pop(), then you will be thread safe.
The concern with using deque in a threaded environment is that there are other methods in that class, and those are not specifically designed to be atomic, nor are they thread safe.
So, while it’s possible to build a thread-safe Python stack using a deque, doing so exposes yourself to someone misusing it in the future and causing race conditions.
Okay, if you’re threading, you can’t use list for a stack and you probably don’t want to use deque for a stack, so how can you build a Python stack for a threaded program?
The answer is in the queue module, queue.LifoQueue. Remember how you learned that stacks operate on the Last-In/First-Out principle? Well, that’s what the “Lifo” portion of LifoQueue stands for.
While the interface for list and deque were similar, LifoQueue uses .put() and .get() to add and remove data from the stack:
>>> from queue import LifoQueue
>>> myStack = LifoQueue()
>>> myStack.put('a')
>>> myStack.put('b')
>>> myStack.put('c')
>>> myStack
<queue.LifoQueue object at 0x7f408885e2b0>
>>> myStack.get()
'c'
>>> myStack.get()
'b'
>>> myStack.get()
'a'
>>> # myStack.get() <--- waits forever
>>> myStack.get_nowait()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<console>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/lib/python3.7/queue.py", line 198, in get_nowait
return self.get(block=False)
File "/usr/lib/python3.7/queue.py", line 167, in get
raise Empty
_queue.Empty
Unlike deque, LifoQueue is designed to be fully thread-safe. All of its methods are safe to use in a threaded environment. It also adds optional time-outs to its operations which can frequently be a must-have feature in threaded programs.
This full thread safety comes at a cost, however. To achieve this thread-safety, LifoQueue has to do a little extra work on each operation, meaning that it will take a little longer.
Frequently, this slight slow down will not matter to your overall program speed, but if you’ve measured your performance and discovered that your stack operations are the bottleneck, then carefully switching to a deque might be worth doing.
I’d like to stress again that switching from LifoQueue to deque because it’s faster without having measurements showing that your stack operations are a bottleneck is an example of premature optimization. Don’t do that.
Python Stacks: Which Implementation Should You Use?
In general, you should use a deque if you’re not using threading. If you are using threading, then you should use a LifoQueue unless you’ve measured your performance and found that a small boost in speed for pushing and popping will make enough difference to warrant the maintenance risks.
list may be familiar, but it should be avoided because it can potentially have memory reallocation issues. The interfaces for deque and list are identical, and deque doesn’t have these issues, which makes deque the best choice for your non-threaded Python stack.
Conclusion
You now know what a stack is and have seen situations where they can be used in real-life programs. You’ve evaluated three different options for implementing stacks and seen that deque is a great choice for non-threaded programs. If you’re implementing a stack in a threading environment, then it’s likely a good idea to use a LifoQueue.
You are now able to:
- Recognize when a stack would be a good data structure
- Select which implementation is right for your problem
If you still have questions, feel free to reach out in the comments sections below. Now, go write some code since you gained another tool to help you solve your programming problems!
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: How to Implement a Python Stack